 Teknologi.id - Every 50 years, there is a revolution in healthcare based on the trends of the era. Healthcare is often considered one of the most conservative industries in terms of technical amendments. After all, there are objective reasons for precautions when human health and even lives are at stake. Nevertheless, more and more practitioners and health services providers acknowledge the importance of technical innovations in healthcare. Modern medicine can’t stay in the last century anymore.
Today people have already got used to electronic medical records or online registration services. But the technical progress in the healthcare goes far beyond, and according to the forecasts, 2019 is going to become a turning point in the adoption of new technologies in medicine, and by 2020, the digital health market is expected to reach $ 206 billion. We have chosen 5 most progressive digital trends that will play an important role in healthcare in 2019 and beyond and want to share them with you.
Teknologi.id - Every 50 years, there is a revolution in healthcare based on the trends of the era. Healthcare is often considered one of the most conservative industries in terms of technical amendments. After all, there are objective reasons for precautions when human health and even lives are at stake. Nevertheless, more and more practitioners and health services providers acknowledge the importance of technical innovations in healthcare. Modern medicine can’t stay in the last century anymore.
Today people have already got used to electronic medical records or online registration services. But the technical progress in the healthcare goes far beyond, and according to the forecasts, 2019 is going to become a turning point in the adoption of new technologies in medicine, and by 2020, the digital health market is expected to reach $ 206 billion. We have chosen 5 most progressive digital trends that will play an important role in healthcare in 2019 and beyond and want to share them with you.
1. Artificial Intelligence
The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in medicine and healthcare is gaining momentum. In one of our previous articles, we have already told how AI robotics is already being used in caregiving. But the iron nurse is not the only implementation of AI-based medical technologies. Ability to process big amounts of data provided by AI together with constantly improving image recognition function have given rise to various innovative health technologies. Here are several directions in which medical AI is going to be used in 2019 and beyond:- Medical diagnosis. AI applications significantly improve the speed and accuracy of the diagnosis. AI tools help to analyze survey data more quickly and accurately, allowing doctors to be more accurate with diagnoses and to see more patients. Today, AI-based image recognition diagnostic devices are already used to diagnose dermatological and optical deviations, diabetes and other diseases which cause appearance changes.
- Medical product development. The process of research and development of new drugs is very slow and expensive. Pharmacists need to take into account hundreds of variables starting from financial appropriateness and finishing with legal and ethical issues. Today, AI is used to safely explore chemical and biological interactions in the drug discovery process based on early-stage clinical data. Among the most prominent examples here are IBM Watson and GNS Healthcare AI system used in the search of cancer treatment.
- Workflow optimization. AI helps to automate such repetitive tasks as routine paperwork, scheduling, and time-sheet entry. These are the task which medical staff often consider to be the most tiresome and frustrating because of their monotony.
2. Big Data & Analytics
Technological advances of the recent years have led to the dramatic growth in the amount of medical and health data gathered about individuals. It creates new opportunities for health organizations in terms of extracting insights from these massive figures. New integrated solutions can gather, process, interconnect, store, and analyze data for any particular purposes. Healthcare professionals use this big data to make the diagnosis quicker and easier. Data analysis can also improve the efficiency within a healthcare organization. And insurance companies can use big data to offer tailored insurance products. The most widespread application of big data in healthcare is Electronic health record systems (EHR). EHR allows keeping a digital record of each person which includes medical history, demographics, laboratory results, diagnoses, etc. Each record is saved in one modifiable file and not only saves doctors from the devastating paperwork but also serves as a valuable statistical source. It also can be used for intervention and provide warnings and reminders when a patient needs new medical examinations or procedures. 94 % of hospitals in the USA are in the process of adoption of EHRs and by 2020, a centralized European health record system is believed to become a reality.
Credit: fancycrave1
3. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to devices connected with each other via the Internet. This technology has seen a significant growth recently. In the healthcare, the IoT is used for remote monitoring of the patient’s or the client’s health through wearables (including ECG and EKG monitors), smart sensors, and mobile apps. By 2020, it is expected that up to 30 billion IoMT devices will be deployed worldwide. IoMT tools help clinicians to monitor patients at home or on the go from any corner of the world. Connected devices are leveraged to monitor at-risk patients to ensure they take medication, measure glucose level and blood pressure, set reminders and alerts. One of the newly-introduced devices of this kind is Apple Watch Series 4 which can monitor heart rate, calm breath, detect falls, count calories and so on depending on the apps installed. Some of the devices, like fitness trackers, correspond to smartphones apps which collect and display necessary statistics.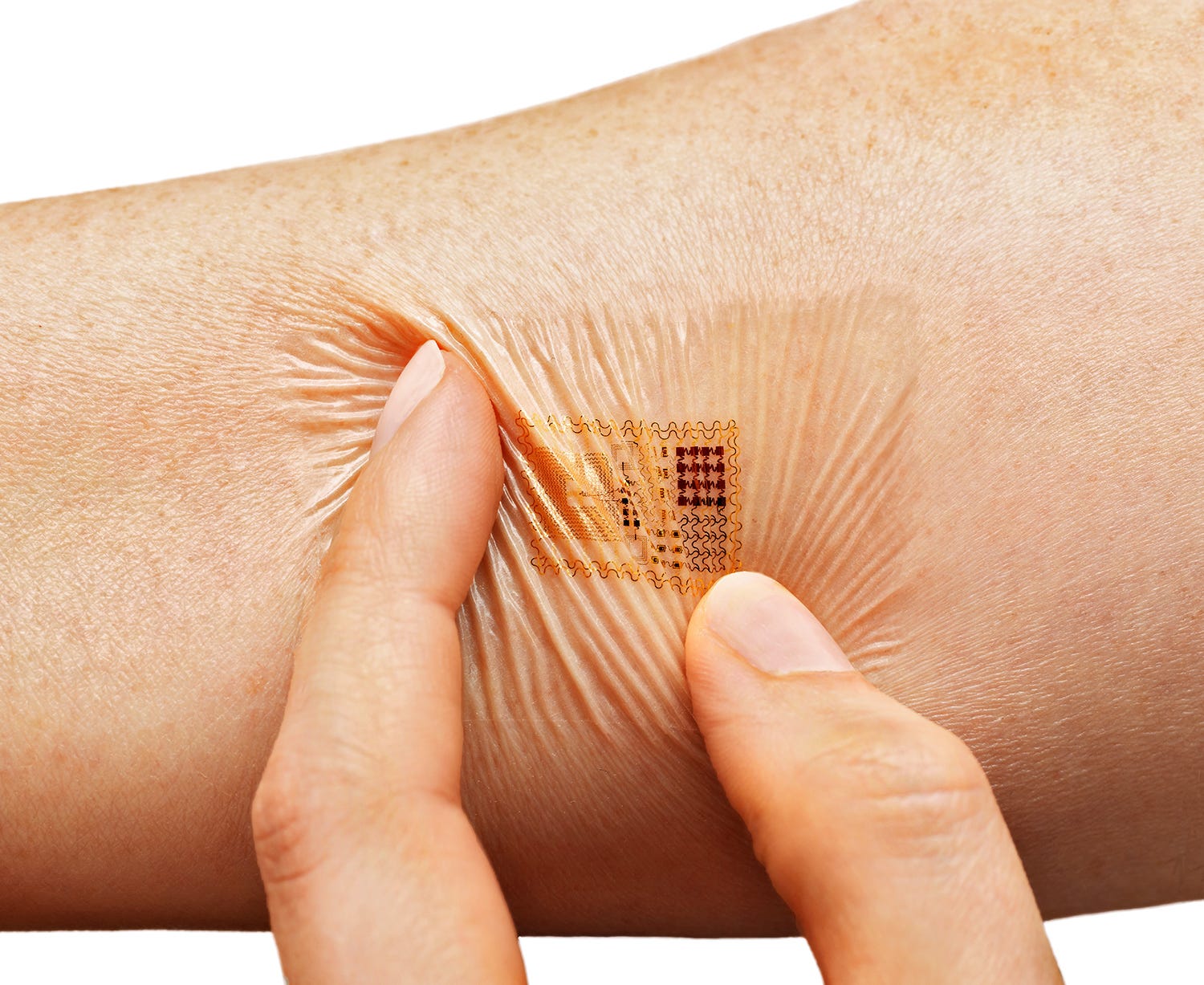
Credit: CT WiFi
4. Telemedicine
Telemedicine improves healthcare by making it easier for patients to get access to specialists. It is especially important in rural or remote areas. According to forecasts, the global telemedicine market is expected to be worth $113.1 billion by 2025. So far, the sector is dominated by video chat platforms. Patients have video calls the physician over the internet which allows them not only describe the symptoms but also show visible symptoms. But this is far from being the only use of telemedicine. The technology provides better conditions for treating and monitoring chronic conditions compared to regular visits to the doctors. It reduces stress for the patients and is more convenient and cost-effective. A unique recent example of telemedicine in action is Southwest Medical. Their NowClinic service is a 24/7 opportunity for clients to have a virtual appointment with a doctor, with a wait time typically less than 10 minutes. The app is available for iOS and Android devices and is easily and quickly installed. This technology allowed SMA to enroll over 30,000 patients within a short period of time.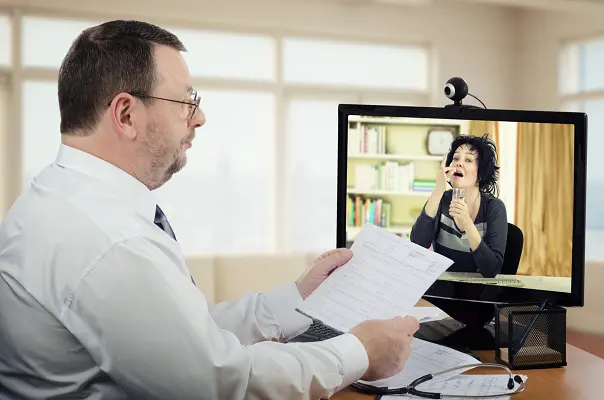
Credit: rightpatient.com
5. VR / AR in the Healthcare
Virtual and augmented reality proposes significant advances to healthcare technologies from diagnosis to medical education and is already used in treatment for the wide range of illnesses. While with virtual reality, the person emerges in totally artificially created surroundings, augmented reality generates images that can be layered on the top of real-world objects. In both cases, the user can see the created imagery or text with the help of VR/AR glasses, while their hands stay free. The major applications of VR/AR technology today are:- Emergency response. Emergency responders allow finding necessary information without wasting time on search while giving the first aid and to record critical information about the patients yet before they arrive at the hospital.
- Prevention and diagnostics. VR/AR allows to model different conditions and manipulate the camera in order to compare the existing examination data with the examples from the database or replicate the effects of treatment.
- Surgery. Here, VR’s most significant impact is in 3D reconstructions of organs in motion. The technology is especially useful when the surgeon needs to work in small spaces or under complicated conditions.
- Education. VR/AR is a great tool which transforms medical education. Surgeons, for example, can rehearse the procedures and exercise precise steps which will allow them to accomplish operations quicker and with minimal damage to tissues in real situations. Microsoft HoloLens is a great example of using VR in medical education:
- Rehabilitation and emotional recovery. It has been already proven that VR/AR has a soothing effect on patients suffering from heavy pains and allows to reduce the use of opioids. In some clinics, like Maplewood Senior Living, VR headsets are applied in the treatment of dementia and cognitive impairments.

Tinggalkan Komentar